
It can also be a predictor of health risks such as diabetes, heart disease, cancers, and more.

3 site skinfold body fat calculator skin#
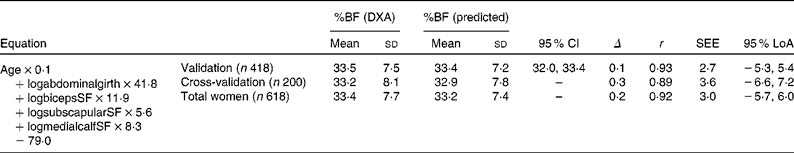
Measuring folds of skin and the subcutaneous adipose fat tissue underneath whether using a caliper or the two-finger pinch method is a consistent and reliable method that’s been used for over 50 years.Ī lot of trainers use this assessment to track their client’s body fat numbers but it’s also possible to do it at home by yourself or ideally using a helper with experience for best accuracy and for the harder-to-reach areas. It appears that assessing overall body composition using a flexed skinfold method does not necessarily improve the overall accuracy of skinfold body composition measurement when compared against a relaxed method.Skinfold testing is one of the most common, convenient, and affordable ways to approximate body fat percentage and body composition (Fat to lean mass ratio). Additionally, both FSM and RSM underestimated body fat percentage as compared to DEXA (FSM: 15.7 + 7.5%, RSM: 16.0 + 7.5%, vs. However, there was a significant difference in thigh skinfold location, indicating that subcutaneous fat measured by FSM was lower than one measured by RSM (FL: 17.5 + 7.2mm, RL: 18.5 + 7.4mm p = 0.003). No statistical differences were observed between FSM and RSM in body fat percentage (FSM: 15.7 + 7.5% vs. A 2 X 3 ANOVA was used to determine the effect of gender (females and males) and different body composition methods (FSM, RSM, and DEXA) along with Bland-Altman plots. The same researcher performed all skinfold measurements and DEXA scan on a single occasion. Each site (chest, umbilical, and thigh for males triceps, super iliac, and thigh for females) was measured three times and the average was utilized to calculate body density and percent body fat. Body composition was assessed by FSM and RSF in a counterbalanced design within gender for RSF and FSM, using Lange skinfold calipers with the Jackson-Pollock 3-site method and the Siri’s percent body fat equation. The current investigation examined the accuracy of a flexed skinfold method (FSM) compared to the traditional relaxed skinfold method (RSF) and DEXA in 20 males (mean age = 20.8 + 2.5 yrs) and 20 females (mean age = 20.8 + 1.6 yrs).

The precise separation of subcutaneous fat from muscle is critical to obtaining accurate measurements of body composition. Skinfold caliper measurements are routinely utilized in assessing individual’s body composition and subcutaneous fat thicknesses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
